Use Next.js with SST
Create and deploy a Next.js app to AWS with SST and OpenNext.
Prerequisites
You'll need at least Node.js 18 and npm 7. You also need to have an AWS account and AWS credentials configured locally.
tip
If you are new to SST, we recommend you start with our latest version instead. Learn more about SST v3.
1. Create a new app
Create a new Next.js app.
- npm
- yarn
- pnpm
npx create-next-app@latest
yarn create next-app
pnpm create next-app
Now initialize SST in the root of your new Next.js project.
- npm
- yarn
- pnpm
cd my-app
npx create-sst@two
cd my-app
yarn create sst@two
cd my-app
pnpm create sst@two
Ready to deploy
Your Next.js app is now ready to be deployed to AWS! Just run — npx sst deploy. But let's take a second to look at how SST makes it easy to add other features to your app.
Start your local dev environment.
- npm
- yarn
- pnpm
npx sst dev
yarn sst dev
pnpm sst dev
Start Next.js
- npm
- yarn
- pnpm
npm run dev
yarn run dev
pnpm run dev
info
When running sst dev, SST does not deploy your Next.js app. You are meant to run Next.js locally.
2. Add file uploads
Let's add a file upload feature to our Next.js app.
Add an S3 bucket
Add an S3 bucket to your sst.config.ts.
const bucket = new Bucket(stack, "public");
Bind it to your Next.js app.
const site = new NextjsSite(stack, "site", {
+ bind: [bucket],
});
Generate a presigned URL
To upload a file to S3 we'll generate a presigned URL. Add this to pages/index.tsx.
export async function getServerSideProps() {
const command = new PutObjectCommand({
ACL: "public-read",
Key: crypto.randomUUID(),
Bucket: Bucket.public.bucketName,
});
const url = await getSignedUrl(new S3Client({}), command);
return { props: { url } };
}
tip
With SST we can access our infrastructure in a typesafe way — Bucket.public.bucketName. Learn more.
Add an upload form
Let's add the form. Replace the Home component in pages/index.tsx with.
export default function Home({ url }: { url: string }) {
return (
<main>
<form
onSubmit={async (e) => {
e.preventDefault();
const file = (e.target as HTMLFormElement).file.files?.[0]!;
const image = await fetch(url, {
body: file,
method: "PUT",
headers: {
"Content-Type": file.type,
"Content-Disposition": `attachment; filename="${file.name}"`,
},
});
window.location.href = image.url.split("?")[0];
}}
>
<input name="file" type="file" accept="image/png, image/jpeg" />
<button type="submit">Upload</button>
</form>
</main>
);
}
This will upload an image and redirect to it!
3. Add a cron job
Next, we'll add a cron job to remove the uploaded files every day. Add this to sst.config.ts.
new Cron(stack, "cron", {
schedule: "rate(1 day)",
job: {
function: {
bind: [bucket],
handler: "functions/delete.handler",
},
},
});
Just like our Next.js app, we are binding the S3 bucket to our cron job.
Add a cron function
Add a function to functions/delete.ts that'll go through all the files in the bucket and remove them.
export async function handler() {
const client = new S3Client({});
const list = await client.send(
new ListObjectsCommand({
Bucket: Bucket.public.bucketName,
})
);
await Promise.all(
(list.Contents || []).map((file) =>
client.send(
new DeleteObjectCommand({
Key: file.Key,
Bucket: Bucket.public.bucketName,
})
)
)
);
}
And that's it. We have a simple Next.js app that uploads files to S3 and runs a cron job to delete them!
4. Deploy to prod
Let's deploy our app to production.
- npm
- yarn
- pnpm
npx sst deploy --stage prod
yarn sst deploy --stage prod
pnpm sst deploy --stage prod
info
View the source for this example on GitHub.
5. Manage in prod
You can use the SST Console to view logs and issues in prod. Create a free account and connect it to AWS.
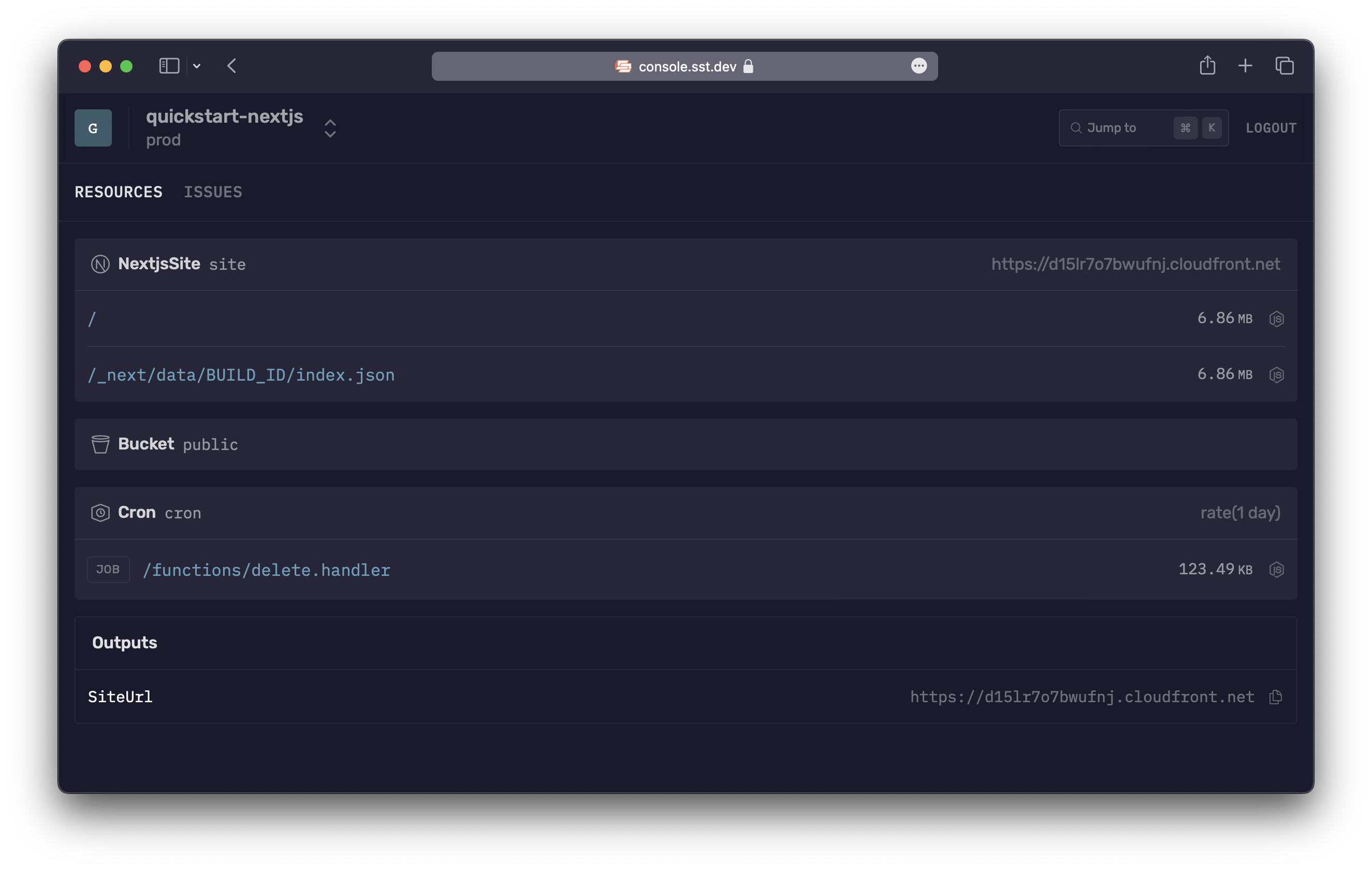
Next steps
- Learn more about SST
Cron— Add a cron job to your appBucket— Add S3 buckets to your appNextjsSite— Deploy Next.js apps to AWS- Live Lambda Dev — SST's local dev environment
- Resource Binding — Typesafe access to your resources
- Have a Next.js app on Vercel? Migrate it to SST.
- Ready to dive into the details of SST? Check out our guide.